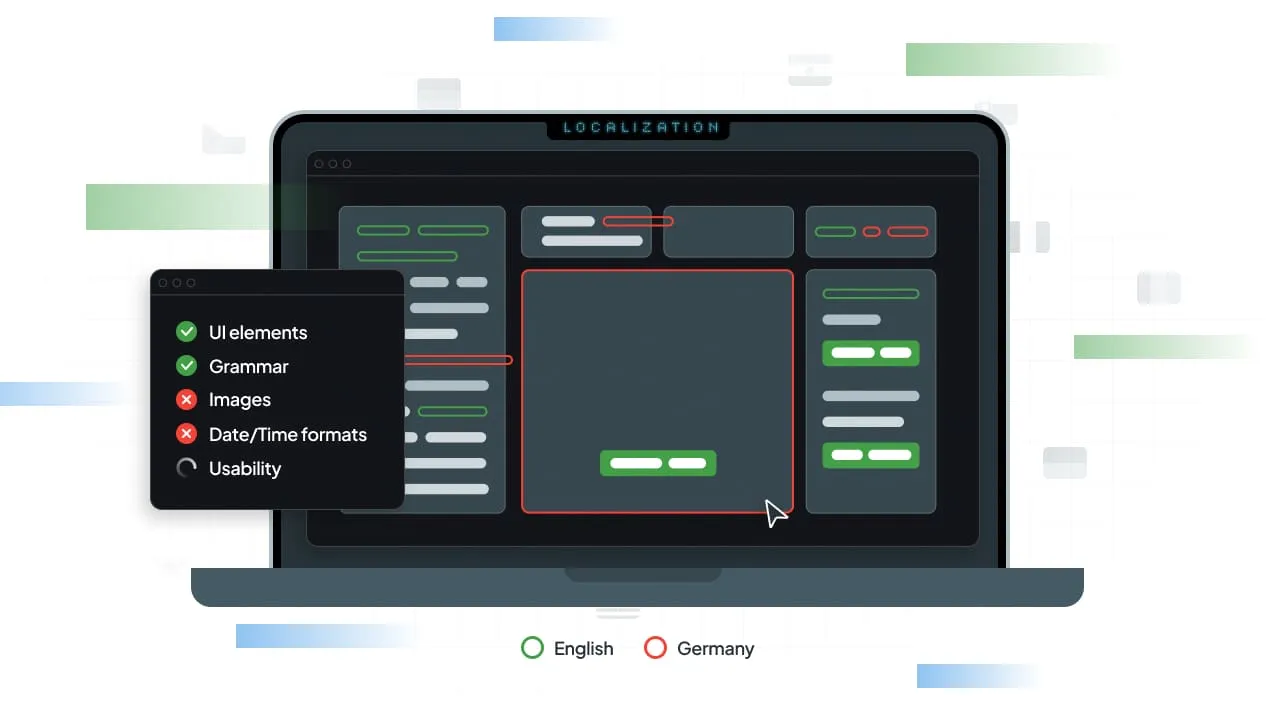
What is the cost of a localization error for a brand? Surely you may think a simple misspelling cannot be that much of a problem. But poor translation quality is a huge business risk that leads to financial losses.
Forbes research shows that with approximately 300 million online shoppers in Latin America, this value potentially equates to over $46 billion in avoidable lost revenue for foreign companies in that region alone.
Just think about it. One error in the UI element can lead to a loss of customer trust. And in the social media era, any error can be the reason for going viral, not for the right reasons.
Unfortunately, the traditional testing environment was built around monolingual products. The software functions properly if you are getting the design action.
However, with multiple target languages, the process becomes much more complicated. That’s why you need to implement localization testing.
In this article, we will explore what localization testing is, why it is important for businesses, how to perform localization testing, and which localization tools to use. Let’s get started.
What Is Localization Testing?
Localization testing, also known as internationalization testing or localization quality assurance, is the process of ensuring the localized products have high quality across all versions for users in different regions.
This process includes adapting all user interface elements for the local language and cultural norms.
Compared to the usual QA that focuses on functionality, localization testing ensures:
- Linguistic validation – grammar correcting, natural sound, brand voice consistency.
- Software functions properly – translations do not interfere with operating systems.
- Visual consistency – no broken layouts, changes in font rendering, or misplaced text.
- Cultural alignment – images, colors, symbols, style, and tone.
- Compliance – terms and other related local regulations.
This is the final stage of the software development lifecycle before the product is launched. The development team ensures the product functions properly, and localization testing verifies that it works correctly for all users.
Why Localization Testing Matters for Business Growth
Skipping testing localization can lead to more than a couple of misspelled phrases. Here are some of the real issues flawed localized content can lead to:
- Low conversion rates. Incorrect checkout data formats will prevent the transaction from being processed.
- Increased support team workload. Badly translated text and software errors increase confusion and the number of inquiries to customer support. This increases the operational costs.
- Brand image damage. An offensive image or a mistranslated slogan can cause controversy and damage brand reputation in the target region.
At the same time, thorough localization testing enables smoother product launches, reduces additional costs, enhances user satisfaction, and fosters a stronger connection with local customers.
Business Case Data: According to CSA Research, about 76% of all customers preferred to purchase from websites in their language. This means that creating multiple language versions is vital if you want to keep and attract three-quarters of all customers.
To put it simply, skipping the localization testing process will not save you money, especially in the long run. Such a practice will not only prevent an increase but also lead to many expensive errors.
3 Types of Localization Testing: Linguistic, Functional, and Visual
Localization testing is a multi-step continuous process that includes three main areas of QA: functional and linguistic tests, and visual QA. The table below provides a quick comparison of these core technical areas.
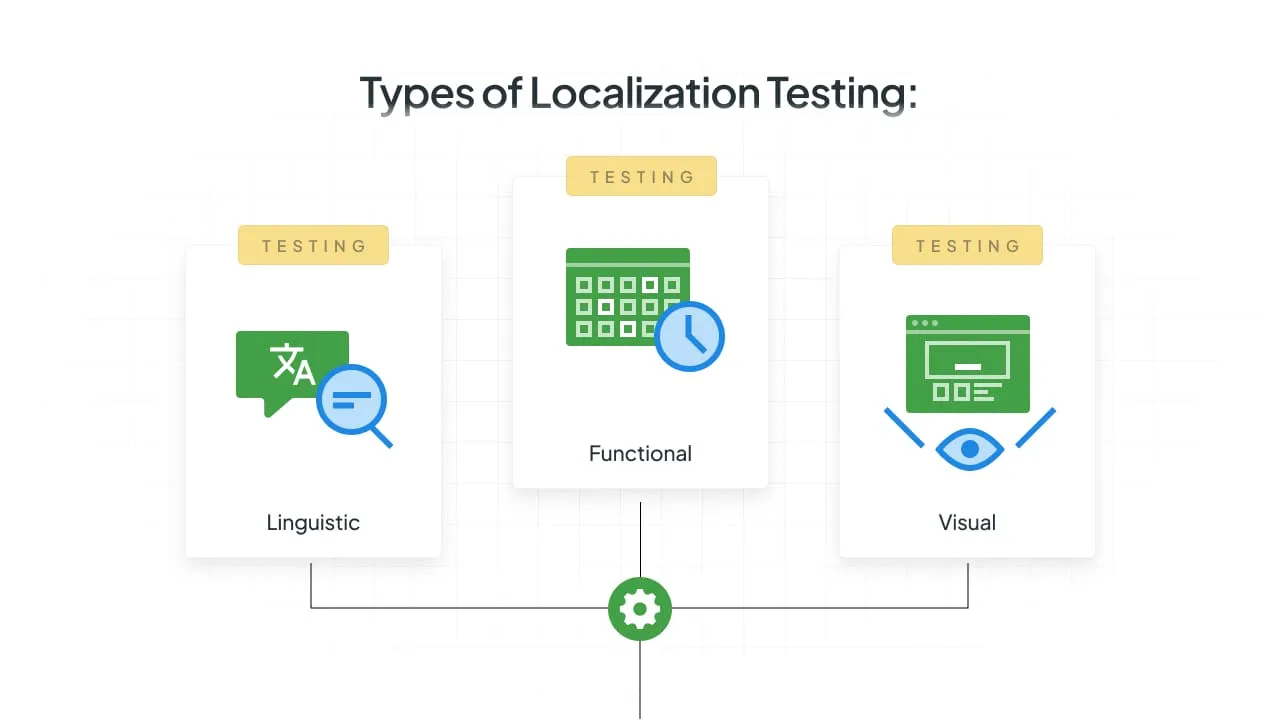
| QA Area | What It Checks | Business Impact Without Such Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Linguistic Testing | Grammar, spelling, terminology, tone, consistency across content. | Looks unprofessional; reduces trust in brand quality. |
| Functional Testing | Whether localized features still work as expected (forms, links, validation). | Failed transactions → direct revenue loss. |
| Visual QA | Layout, font rendering, text expansion, alignment, UI breakages. | Frustrating UX; lower conversion rates if users can’t complete actions easily. |
These areas do overlap. The next section will expand on these core areas with a comprehensive checklist, including cultural and formatting requirements.
Localization Testing Checklist

1. Linguistic and Translation Testing
Linguistic and translation testing are the most obvious when it comes to adapting software to the local culture. The process includes ensuring there are no typos, grammar issues, or awkward phrasing. At the same time, brand voice and consistency must be kept.
Common Issues:
-
Literal translations. Either a lack of experience or the use of machine translation alone can result in phrases that are incorrectly translated and carry different contextual meanings.
Example: Translating the English phrase “checkout” (for payment) literally into a phrase in another language that means “check out” (as in, leaving a hotel).
-
Terminology inconsistency across projects, features, and web pages.
-
Wrong tone and style where formal/informal language is expected.
Business Impact:
- Loss of trust and respect from customers
- Constant misunderstandings
- Brand image damage
2. Cultural Appropriateness
Simply translating content is not what localization is about. You must also adopt visual imagery, color design, and the elements to fit the culture and expectations of the target market. Meanings, humor, and associations can differ from region to region.

Common Issues:
-
Hand gestures with different meanings
-
Opposite color meanings (red can be a symbol of warning as well as prosperity)
Example: Using a white color scheme for a wedding-related application in a culture where white is the color of mourning, instead of celebration.
-
Slogans that are not adapted to the target language
Business Impact:
- Negative brand association
- Lost respect and trust
3. User Interface (UI) and Visual Integrity (Visual QA)
One of the most common worldwide issues that can disturb the UI is text length and character size. Languages like German can take up 30% more space than English. Languages that use hieroglyphs can require completely different font rendering or layout.
Another critical issue is buyer habits. Customers around the world may have varying expectations about how an e-commerce website and the purchasing process should appear.

Common Issues:
-
Text overflows because of the layout and length difference
Example: A button labeled “Add to Cart” (11 characters) fits perfectly. Its German translation, “In den Warenkorb legen” (20 characters), wraps or runs off the screen, breaking the visual appearance.
-
Incorrect font rendering with missing characters
-
Confusing UI for the target market
Business Impact:
- Churn caused by poor usability
- Increasing customer confusion that drags conversion down
- Unexpected costs caused by additional development processes
4. Functional Integrity of Localized Versions
Localization efforts should be channeled at all product lifecycle processes. Without effective localization testing, simple date format changes can lead to payment validation errors. This can cause not only a revenue decline but also a loss of trust from the locals, creating a sense of fraud.
Common Issues:
-
Inability to add a phone number because of the one-region-designed forms
Example: A sign-up form is hardcoded to accept only 10 digits (like the US format). A user from another region with a longer national phone number (e.g., 11 or 12 digits) is blocked from signing up.
-
Failed payments due to unsupported currency formats
-
Hyperlinks to the untranslated or broken webpages
Business Impact:
- Loss of revenue from failed transactions
- Brand image damage and loss of customer trust
- Increases customer support inquiries
5. Local Formatting (Dates, Currencies, and Compliance)
Some small formatting details may seem unimportant, yet they can severely impact users’ trust and cause purchasing errors. Date, time, currency, and address formats must be adjusted accordingly.
Local laws and regulations should also not be ignored. They may require specific formats or information to be displayed.
Common Issues:
-
Confusing date formats (MM/DD/YYYY in the US, DD/MM/YYYY in Europe)
-
Misplaced or missing currency symbols
Example: Displaying the US currency format as $100.00 in a European market where the standard is 100,00 $ or 100,00 €
-
Addresses not aligned with local standards (postal codes, province/state fields).
-
No disclaimers required by local regulations.
Business Impact:
- Increased cart abandonment
- Legal penalties for the missing information
- Increased delivery costs because of the failed shipments
Localization Testing Workflow
Localization testing keeps evolving together with the software. It’s a complex process that is integrated with many elements.
To ensure quality outcomes, testing localization requires a workflow that starts at the early design stages, alongside development, and continues after product launch. Such an approach reduces the possibility of late-minute inconsistencies, accelerates time-to-market, and ensures consistent quality across all localized versions.
We have outlined a step-by-step workflow that helps integrate testing efforts into all stages of the product lifecycle.
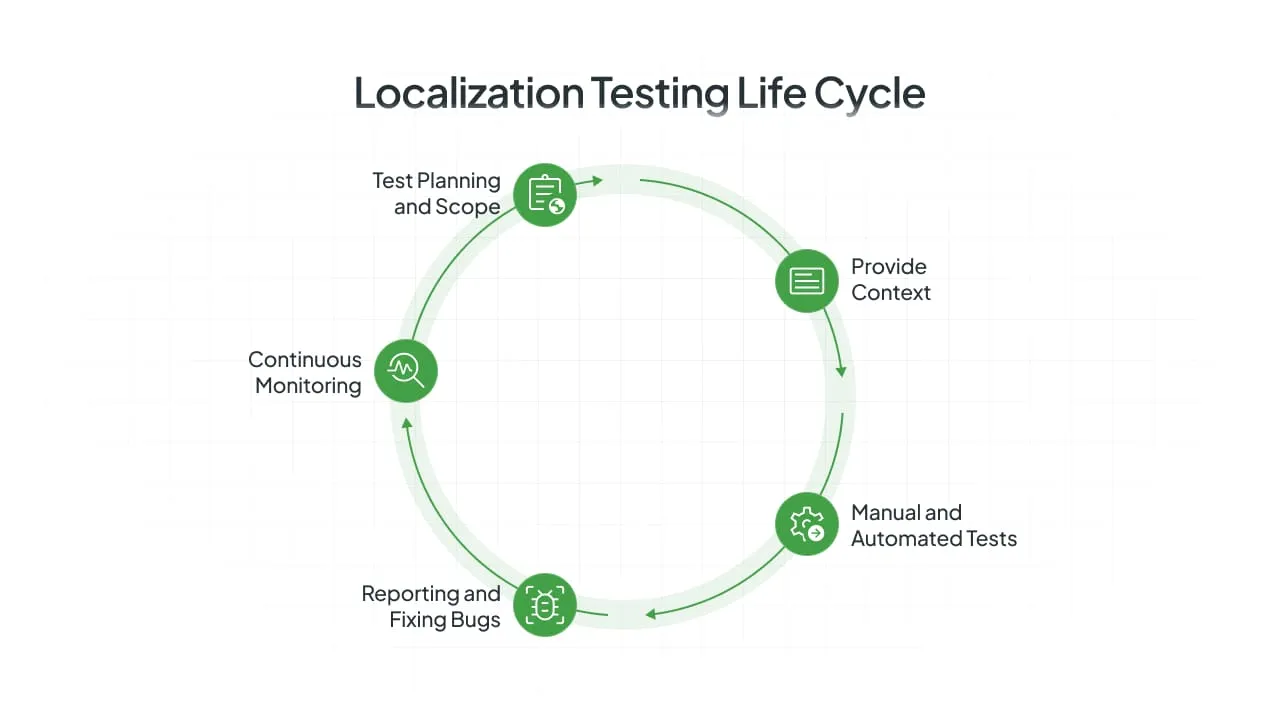
Step 1: Localization Test Planning and Scope
The workflow starts before any translation begins by creating a plan for your team to follow. Preparation is vital and allows businesses to save time and ensure the team has a clear understanding of the procedure.
Key Preparation Activities
To ensure an efficient localization project and quality outcomes, you must establish clear guidelines and test the foundation of your product:
- Define the Scope: Clearly state what will be localized and tested, including target languages, specific features, and operating systems.
- Prioritize Target Markets: Align your company’s business goals with the testing efforts to define which markets have the highest priority.
- Create a Universal Checklist: Develop a reusable list covering all essential localization testing areas: linguistic, cultural, UI/visual, functional, and formatting.
Implement Pseudo-localization
Pseudo-localization is an essential technical preparation step where source strings are artificially modified to simulate a localized language. This process does not involve actual translation but intentionally introduces common localization challenges to test the software’s technical limits early.
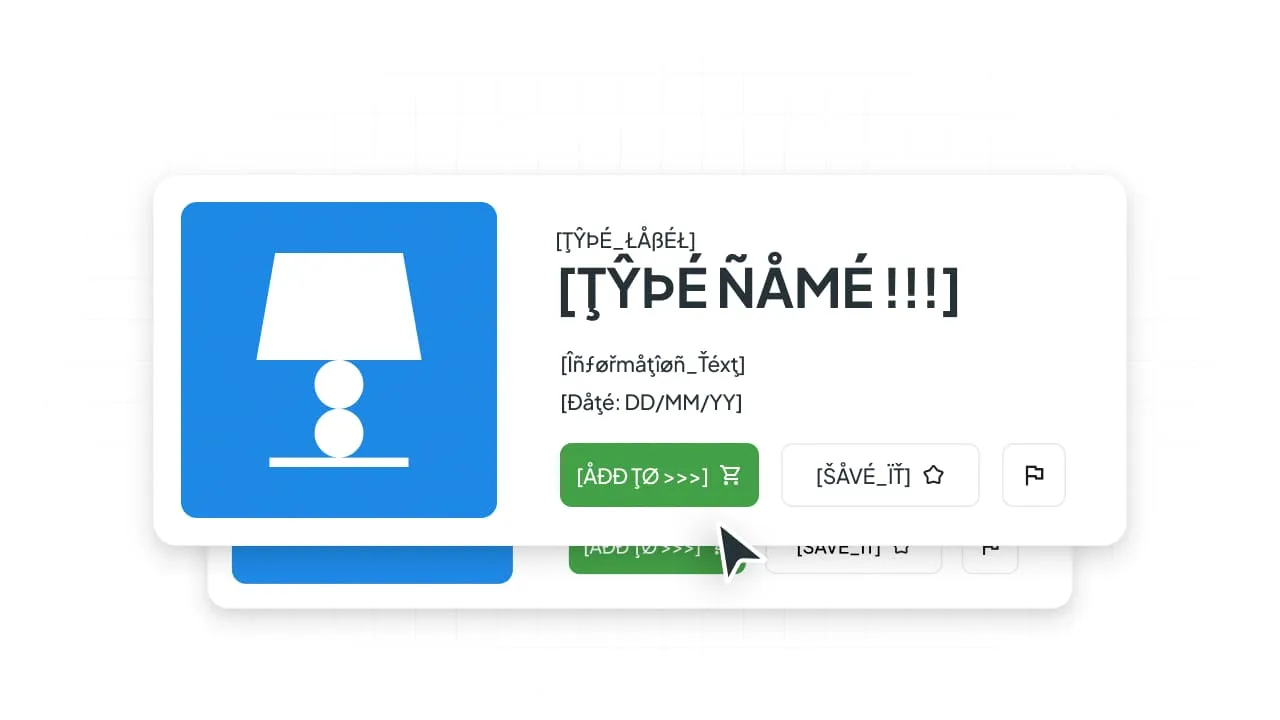
- What it does: Characters are expanded (e.g., “Settings” becomes “[Šëééñtttiñgssššš]”), special characters are added to check for font/encoding issues, and text direction might be reversed (e.g., for Right-to-Left languages).
- Why it’s necessary: It quickly reveals potential issues like UI breakage, cut-off text (due to expansion), encoding problems, and hardcoded strings (text that was incorrectly embedded directly in the code instead of being externalized for translation) before professional translators begin work.
Step 2: Equip Your Team with Context
Understanding context is key when adapting a product for different regions. Providing your QA teams with tasks and no explanation can lead to more errors. Without context, even native speakers may miss subtle mistakes.
Here’s where translation management software like Crowdin can help. A TMS provides In-Context Preview, showing translation memory suggestions and allowing testers to instantly spot text overflow or layout issues. It also links strings to screenshots, enabling testers to verify translations align with UI constraints.
Learn how Bounce implemented a solution for managing project screenshots.
Step 3: Manual and Automated Tests Execution
After thorough preparation and providing your team with the required software, it’s time for the actual testing process. The most effective way to ensure accuracy and efficiency is to implement a combination of manual and automated tests.
Manual Testing with Native Speakers
Native speakers and professional translators bring cultural and linguistic validation that no software can provide. It’s important to receive native user feedback early in the process. They may help with:
- Removing any inappropriate tone and slang
- Keeping cultural nuances that cannot be translated or adapted
- Ensuring the language sounds accurate and natural to the locals
Automated QA Checks
Automated tests help limit the amount of repetitive checks, allowing testers to focus on higher-value tasks. Automation features within the TMS can help with:
- Flag placeholder errors (
%s,{username}) - Detect untranslated strings
- Check punctuation consistency
- Validate the glossary consistently and adherence
Step 4: Reporting and Fixing Bugs
Testing can only be as efficient as the process of bug reporting and its resolution efficiency. This is true for both localization and a traditional testing environment. Vague bug reporting can lead to delays and increased development costs.
Best Practices for Bug Reporting
- Provide screenshots and a screen recording to represent the issue accurately.
- Provide the context for the issue, and what the correct output should look like.
- Implement software integrations. Crowdin integrates with Jira, GitHub, Slack, and other tools, which ensures localization bugs flow directly into existing development workflows.
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring After Launch
Product launch does not mean the end of testing localization. Products keep evolving with new updates and features, adapting to the latest trends and requirements. A continuous localization workflow also includes post-release monitoring.
Strategies for Continuous Monitoring:
- Monitor customer support inquiries with questions about language or formatting
- Collect used feedback from the target markets
- Collect continuous analytics – a change in conversion can be a signal of localization issues.
- Schedule regular regression testing with every new release.
Continuous Testing
A unified platform like Crowdin is a pillar of continuous localization testing. By integrating its QA with translation and development departments, a business can achieve :
- Shorter release cycles – Localization testing runs in parallel, not after development.
- Fewer production issues – Automated QA catches repetitive mistakes before they go live.
- Stronger global user retention – Consistent, high-quality localization builds trust.
Build Your Localization Testing Tool Stack
Even the best QA localization strategy fails without the right localization testing tools. With the effort focused on linguistics, UI/UX, functionality, and compliance, tools that can integrate with your workflows become essential.
Automated tools can help you improve the quality and efficiency of the processes, which contribute to continuous international growth. In this part, we will go over the main localization testing tools every QA team needs.
Crowdin as the Unified Translation Management System (TMS)
TMS is the #1 tool for localization testing. Crowdin centralizes all localization data, context, and QA checks, minimizing errors and promoting cross-team collaboration.
As your TMS, Crowdin provides an advanced suite of QA capabilities:
- In-Context Previews. Translations are displayed the same as inside your app, website, or game, allowing testers to spot layout issues instantly.
- Automated QA Checks. All placeholder errors, untranslated strings, terminology mismatches, and punctuation errors are automatically highlighted.
- Screenshots Linked to Strings. Testers can validate translations with UI screenshots and catch any inconsistencies.
- Comments. Localization testers can leave comments for linguists directly within the platform for quick issue resolution.
- Integrations. Crowdin offers integrations with common platforms, including Jira, Slack, and CI/CD pipelines.
Automated Visual Testing Tools
Accurate translations are vital to product localization. However, when the translation interferes with the design, user satisfaction and experience can be negatively affected. One of the efficient solutions is the use of visual testing tools.
Here’s how they work:
- Take screenshots of the software across localized versions.
- Screenshots comparison to detect inconsistencies: layout breaks, text overflow, or cut-off elements.
- Highlighting localized content inconsistencies.
Compared to the standard screenshot tools that are not connected to localization, Crowdin automatically links strings to screenshots. This eliminates the need to manually compare since the context is highlighted.
Testing Management and Bug Tracking Tools
Such a complex process as localization testing cannot be effectively performed without a unified structure. A centralized system that facilitates project management testing helps ensure all areas are covered and prevents duplicate reporting.
The main features include:
- Workflow organization for linguistic, functional, and visual QA
- Access to previous test cases that help monitor recurring issues.
- Collaboration features for task assignment and faster issue resolution.
If a translation error is highlighted in Crowdin, it will automatically appear in Jira, along with the context and screenshots.
How to Automate Localization Testing
Automations in localization testing play a vital role. The key is to strike a balance between automation and human expertise. This allows us to get the most out of both approaches, improving both efficiency and accuracy.
What to automate:
- Missing translations: Automatically flag empty or untranslated strings.
- Placeholder validation: Ensure test script variables, such as
%sor{username}, remain intact. - Punctuation and spacing: Highlight common formatting errors, including double spaces or missing periods.
- Terminology consistency: Ensure the terms are correct and consistent across all content.
- UI regression checks: Use automated screenshot comparisons to detect layout changes between builds.
What is better handled by human experts:
- Cultural nuance: Humor, idioms, and symbols that may be offensive or confusing for some international markets.
- Tone and style: Whether the content feels natural, on-brand, and aligned with local expectations.
- User empathy: How real users perceive and emotionally connect with the localized product.
The hybrid approach remains the best strategy. Companies implement automation tools to track repetitive, mechanical errors and work with natives and linguistic experts to ensure cultural norms are intact.
Conclusion: Quality Testing – the Core of Your Business Strategy
Localization testing shouldn’t be just another task on our checklist that must be confirmed before product launch. By covering key areas, implementing a strategic workflow, and supplying your testing team with quality software tools, you can:
- Prevent costly errors before launch.
- Create relevant and consistent user experiences.
- Build trusting and long-lasting relationships with users around the globe.
Translating text into the local language is only one of the main parts of localization. Without commitment to quality at every stage, success cannot be achieved. Localization testing is the process that ensures your product performs as designed on every market, expanding your business worldwide.
Localize your product with Crowdin
FAQ
Who is a localization tester?
A localization tester is a QA specialist who specializes in ensuring the product performs at the same high quality in different languages and for every international market. During the testing, they cover linguistic accuracy, proper functions, visual integrity, and other elements of the interface that influence user experience.
How can I automate localization testing?
Within the localization testing process, businesses can automate repetitive tasks that include looking for mistakes, calendar placeholders, and punctuation, as well as checking visual imagery. Keep in mind that aspects such as nuance, tone, and context can only be covered by human specialists.
- What are the best practices for localization testing in software development?
- There are several best practices, including:
- Implementing testing early in the workflow
- Continuous testing even after product launch
- Implementing a Translation Management System (TMS) like Crowdin for in-context previews and QA checks.
- Working with natives and linguistic specialists
- Creating a universal checklist that covers the main localization testing areas
- Detailed bug reporting
Is localization testing functional or non-functional?
Localization testing involves both types of processes. Functional includes checks of the system performance. Non-functional verifies more nuanced aspects like usability, relevance, time, and consistency.
Akanksha Babbar
Localization Engineer at Yara International (ex. Localization Senior Analyst at Dell International).