This article will explore the world of computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools. We will discuss their types, features, benefits, examples, and how to choose the best tool for your needs. Whether you are a translator, a project manager, or simply interested in language technology, read on to learn how CAT software can assist your localization.
*For further clarity, we use ‘CAT Tool’ and ‘CAT Software’ as the same concepts in this guide.
Before we dive into the details, check out this summary on the guide of CAT software:
- Definition: CAT tools are software applications designed to technologically support translators and make their translation process faster, more organized, and consistent.
- Main types: 1) Desktop-Based (installed locally for offline work), 2) Cloud-Based (used online via a browser), and 3) Hybrid (a blend of online and offline capabilities).
- Key benefits: Increased productivity and decreased costs with Translation Memory (TM), enhanced brand consistency and translation quality via Terminology Management and automated QA checks, and better teamwork with collaboration features.
- The workflow includes project setup (defining languages, resources, and teams), importing source files, segmenting content into manageable parts, translating phases, collaborative review and editing, and exporting the completed translations in the needed format.
- How to choose the best software: Evaluate the project’s specific translation requirements (like volume and languages), file formats you need to translate, necessary collaboration and project management features, your budget, and the provider’s data security and compliance standards.
What Is a Computer-Assisted Translation Tool?
A computer-assisted translation (CAT) tool is software that helps human translators to convert the meaning of words from one language to another. Its primary goal is to make the localization and translation process more cost- and time-efficient.
From their origins as basic desktop solutions in the mid-20th century, CAT tools have evolved into rich, often cloud-based platforms that became essential for modern localization.
The CAT tool doesn’t replace the translator but helps them work better and faster. These tools help translators work with smaller, manageable units, often sentences or paragraphs, which makes the translation process more organized. CAT tools are helpful in any localization case, from marketing materials to software.
3 Main Types
Typically, there are three types of CAT tools: Desktop-Based, Cloud-Based, and Hybrid. Here is the table that compares all three together based on the CAT tools’ features:
| Feature | Desktop-Based | Cloud-Based | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Mode | Offline (local install) | Online (browser access) | Online with offline sync |
| Collaboration | Limited / Manual | Real-time / Built-in | Real-time (online); Sync caution (offline) |
| Accessibility | Single device | Any device with internet | Any device (online); offline mode may vary |
| Advantage | No internet is needed | Teamwork & access from anywhere | Flexible online/offline use |
| Disadvantage | Isolated work | Requires stable internet | Potential sync conflicts |
Examples
A few of the most popular CAT tools include:
- Crowdin (all-in-one localization tool with CAT functionality)
- Trados
- Wordfast
- MemoQ
- Smartcat
- OmegaT
"The CAT tool market is booming, projected to reach USD 4.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.7%. (Source)
CAT Features & Benefits
The main goal of computer-assisted translation tools is to provide translators with features that improve translation efficiency and consistency. Let us discuss the most popular CAT features and the benefits each brings.
Productivity with Translation Memory (TM)
Translation memory is one of the fundamental features; this intelligent database stores all your previously translated segments, sentences, phrases, or even individual words, along with their source counterparts. When a similar or identical segment reappears in a new document, your CAT tool can suggest the previous translation or add it immediately. The translator can accept, modify, or reject suggested translation. (For more information, read how translation memory works). Localization tools now go even further: using AI localization and machine translation to suggest context-aware translations for segments that don’t have a match in memory.
Benefits:
Research paper from Cologne University of Applied Sciences indicates that using translation memory can reduce translation delivery time by an average of 50% and decrease translation updates by 20–30%.
Branding and Quality Consistency
Terminology Management: CAT tools allow users to create and manage localization glossaries or terminology databases. This ensures that industry-, client-, or brand-specific terms are used consistently, often complemented by style guides that define tone, voice, and grammatical preferences for each language.
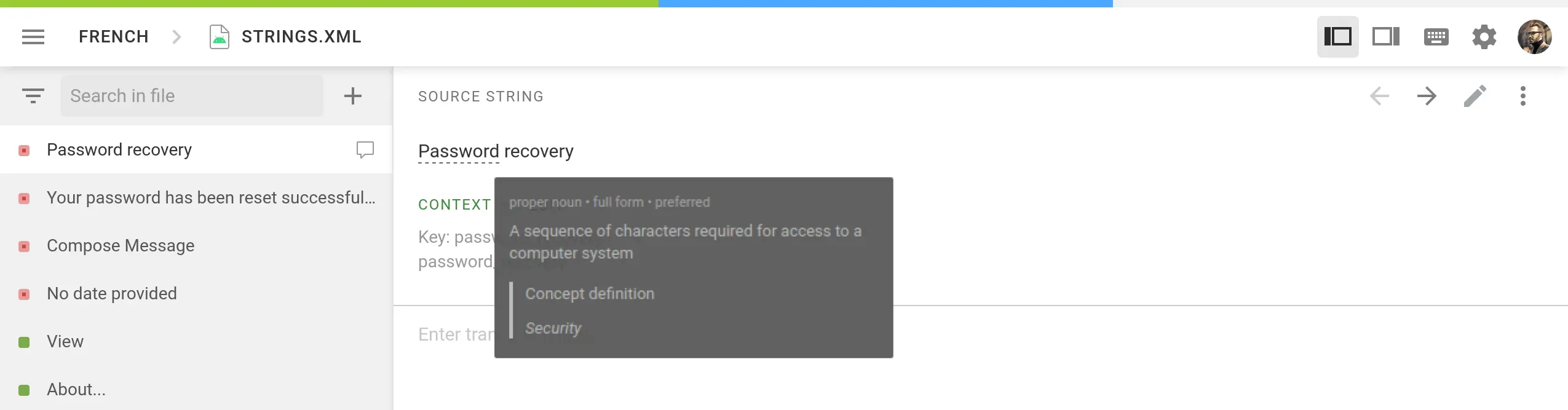
Quality Assurance (QA) Checks: translation QA checks in CAT tools automatically identify a wide range of issues. These can include spelling/formatting/grammar/terminology mistakes, and more. Issues can be highlighted for the translator during translation or for an editor during the review.
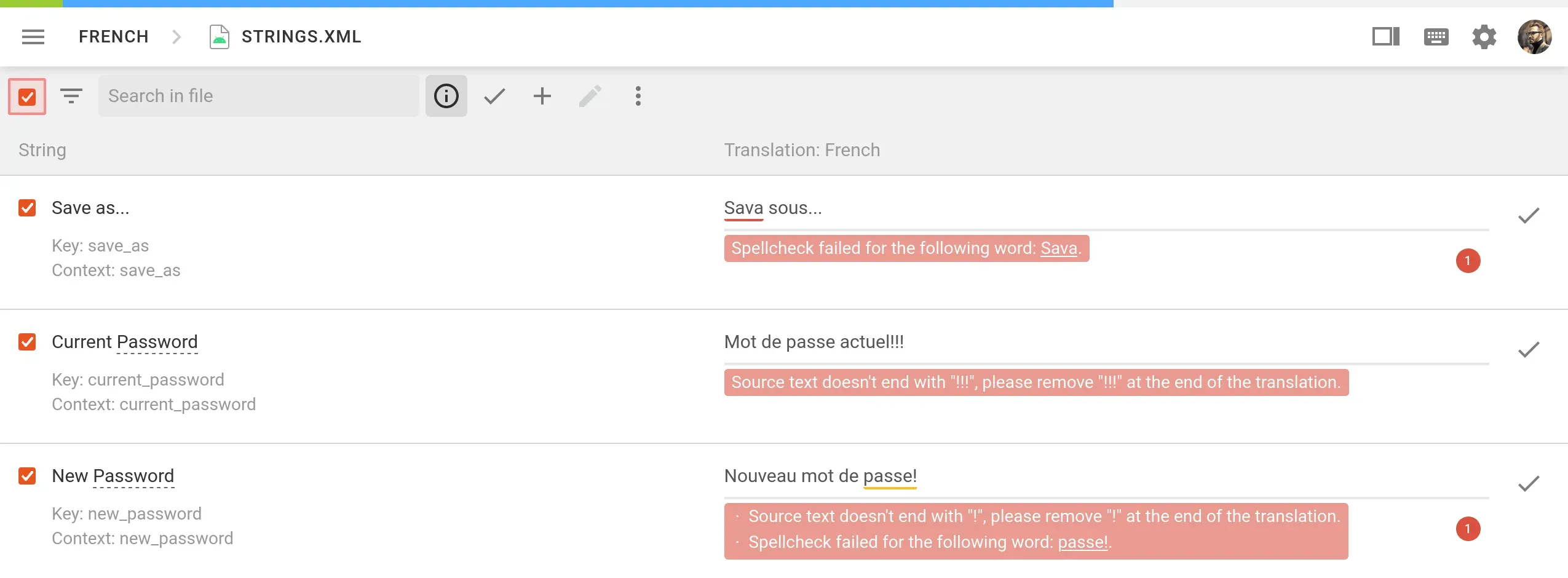
There are also industry-standard metrics that help you evaluate translation quality, for example:
Some tools support them as an add-on to analyze the translation quality.
Benefits:
-
Higher Translation Quality: Fewer errors and inconsistencies lead to more accurate translations.
-
Consistent Brand Messaging: Keeps your brand’s voice and terminology maintained across all languages and markets.
Collaboration and Versioning
Real-time Collaboration: translators, editors, proofreaders, and project managers can simultaneously work on the same project files. Comments and discussions on specific strings, resources (TMs, glossaries) are all in one place.
Version Control: Say goodbye to confusing file names like source-file1-copy-final-FINAL.xml. Cloud CAT tools manage versions centrally, so everyone always works on the latest iteration. If you add 10 new strings to a file, only those new strings will need translation, while all already translated content remains intact and accessible to the entire team.
Benefits:
- Team Productivity: Live access and clear communication reduce bottlenecks.
- Project Transparency: Everyone involved can see progress and access the same information, which leads to better coordination.
- Content Integrity: No errors caused by working on outdated or incorrect file versions.
Broad File and Language Support
Wide File Format Compatibility: Leading CAT tools support many common localization file formats: JSON, XLIFF, XLSX, CSV, XML, YAML, HTML, Markdown, and many more. Therefore, you can handle content from websites, software/mobile applications, technical documentation, marketing materials, and beyond. When choosing the tool, consider its ability to support your current and future file format needs.
Language Capabilities: Most CAT tools support a wide range of languages, often allowing you to add custom languages or regional variants if needed. Correct language settings are extremely important as they influence how translated files are structured and exported. Translation files can use different language codes. For example:
- Two-letter code: en for English, fr for French.
- Three-letter code: eng for English, fra for French
- Country codes: en_US for American English, en_GB for British English, and fr_CA for Canadian French.
Benefits:
Project Versatility: Work on any localization project, no matter the type of content.
Scalability: Choose a tool that can grow with your business and support new languages and file types.
Data Security
Security Standards: A good CAT tool provider prioritizes data security and complies with recognized data protection standards. Security standards to check for:
Application-Level Security: Besides compliance, look for built-in security measures such as IP address allowlisting, Single Sign-On (SSO) integration, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), and a secure REST API for integrations.
Benefits:
Confidentiality: Your sensitive information is protected throughout the translation process.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps your organization meet its legal and contractual obligations.
Builds trust with clients and stakeholders.
Computer Assisted Translation Examples
See how computer-assisted translation is being used in practice.
1. Software
Challenge: Frequent software updates that require a continuous localization workflow to avoid slow manual syncing.
CAT Solution:
- Automated sync with code repositories (e.g., GitHub, GitLab).
- Translation Memory (TM) for UI and consistency.
- In-context previews for accurate UI translation.
2. Technical documentation
Challenge: Long, repetitive technical manuals that require frequent, costly, and time-consuming translation updates.
CAT Solution:
- Translation Memory (TM) extremely decreases re-translation.
- Terminology Management for term accuracy.
- Automated Quality Assurance (QA) for error detection.
3. Marketing Materials
Challenge: Multilingual marketing campaigns (ads, web, email) with tight deadlines that require brand voice and message consistency across all markets.
CAT Solution:
- Shared Translation Memories & Glossaries for brand alignment.
- Cloud-based collaboration for real-time teamwork.
- Workflow automation for managing a large number of campaign assets.
Business Impact
Beyond operational benefits for translators, CAT tools are strategic assets that contribute to overall business translation objectives for multilingual companies:
| Benefits | Factors |
|---|---|
| Faster Time-to-Market | Reusing translations, efficient workflows |
| Improved ROI and Cost Control | Reduced translation spend, less rework |
| Stronger Brand Consistency and Trust | Consistent terminology and quality |
| Higher Scalability Potential | Easly managing more volume/languages |
| Reduced Risks | Higher quality localization from the start |
How Does CAT Software Work?
Most CAT tools work by breaking up the source text into chunks (often sentences) and showing each chunk in a way that is easy to read.
Details may differ. However, most tools follow this typical workflow.
1. Project Setup
Сreate a new translation project. Choose the project’s source and target languages, your translation strategy, team, types of content (formats), and deadlines (if any).
2. Import the Files
Import the files that need translation into the tool. Most CAT tools have three options for file upload: manually, using API, or using integrations. For instance, Crowdin has 600+ apps and integrations to automate syncing with existing content repositories (CMS, code repositories, help desks, etc.).
Plugins and integrations can automate various aspects of the localization process (like content updates and synchronization), which saves time and reduces manual work.
3. Segmentation
CAT programs can automatically divide the source material into smaller sections, such as sentences or paragraphs. Segmentation enables translators to translate unit by unit and promotes context consistency.
4. Translation
Translators begin to translate the target segments into the target language. They now use a user-friendly interface, not a coding environment. They may also use the tool’s translation suggestions.
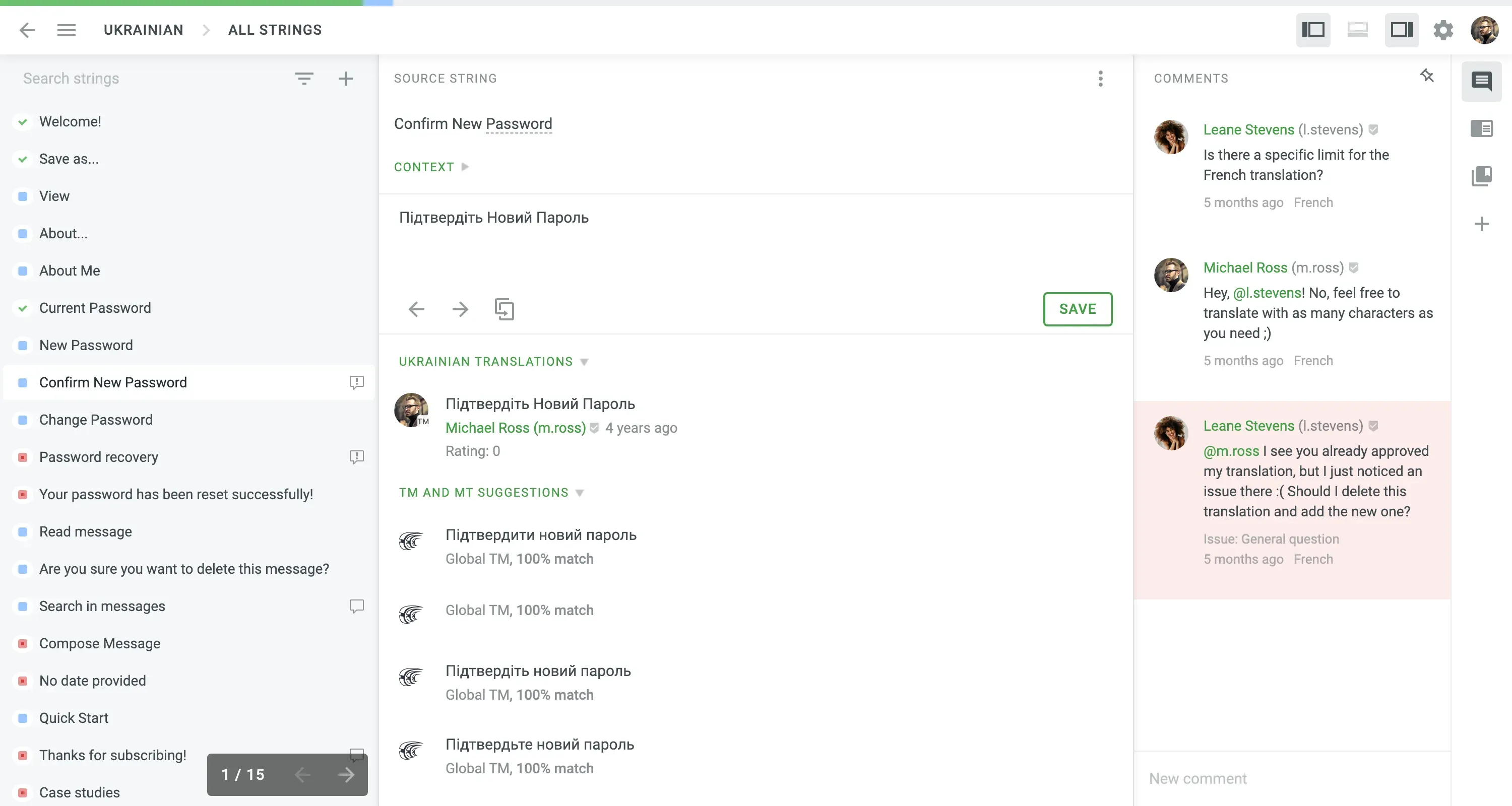
5. Collaboration and Review
Edits and suggestions are synchronized in real-time, facilitating efficient teamwork. After the translation, a final review takes place, which checks if the content is accurate, consistent, and follows the project requirements with style guidelines.
6. Export
Export the final translated document, usually in the same format as the source document or as noted by the client.
7. Feedback and Improvement
Such tools often provide reporting and analytics to track project progress and translation quality with performance. Feedback is used to improve future projects and maintain translation quality.
CAT Tool vs. Translation Management System (TMS)
| Aspect | CAT Tool | TMS | Crowdin’s Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal | Aid translator efficiency and text consistency | Manage translation projects & workflows | Unified platform for both translation & management |
| Primary User(s) | Translators, Editors | Project Managers, Localization Teams | All stakeholders (Translators, PMs, Devs, Marketing) |
| Functions | Translation Memory, Terminology, Segmentation, In-Editor QA | Workflow Automation, Resource/Vendor Mgt, Reporting, API and Integrations | Both, connected within one environment |
| Scope | At the string/document translation level | Entire localization lifecycle, multiple languages/files | Full-scope localization projects, continuous or agile |
| Main benefit | Increased translator productivity and content consistency | Enhanced project management, automation and scalability | Efficiency, collaboration and control |
| Deployment | Desktop, Cloud-based, or Hybrid | Primarily Cloud-based | Cloud-based with wide collaborative features |
How to Choose the Best CAT Translation Tool
Selecting a good tool can result in extreme time and quality gains. Here are our practical suggestions for choosing smarter:
1. What are your needs and scope?
Before thinking about features, understand what you need the tool to do.
- Project volume: How much content do you need to translate, in how many languages, how often, and what about formats?
- Team count and structure: What is the size of your translation team? What is the structure, are they in-house, freelance, or both? Do you need collaboration features?
- Budget: Some CAT tools are free for open-source and educational projects, like Crowdin. If you have a private project, plans start with the limited free subscriptions to the wide enterprise subscriptions.
2. Functionality
Analyze how different tools compare in translation capabilities. (Many of these were described in the previous section; here, you are making them selection criteria.)
- File format support: Does the tool have integrations/capabilities to translate all your file formats (e.g., XLIFF, JSON, XML, XLSX, HTML, Markdown, etc.)?
- Feature set: Not only are Translation Memory and Terminology Management important, but does the tool offer QA checks, customization options, and integration capabilities (API, connectors to CMS, code repositories, etc.) that are crucial for your project?
- Collaboration and project management: If teamwork is important for you, check for features like real-time collaboration, task management, and progress tracking.
- Security: Does the tool meet your data security requirements (e.g., GDPR, ISO 27001)?
- Scalability: Analyze its ability to handle more users and larger volumes, as well as its ability to grow with you.
3. Provider reputation and usability
- Research: Go further than marketing materials. Read genuine user reviews, read case studies, and check community forums.
- Testing: Most providers offer free trials and/or demos with their business development teams. Use these to test the usability of the tool.
- Support and training: Review the quality of customer support and if the training resources and documentation are clear.
Tips from Crowdin
- Consistency from the beginning: Develop styling guides, glossaries, and formatting rules right from the start of your project.
- Match settings to your workflow: Do not just use default ones. Customize segmentation rules, QA check sensitivity, and other preferences to align the tool with your team’s processes.
- Use collaborative features: If using a cloud-based tool, fully utilize its real-time collaboration capabilities. Facilitate active communication (e.g., in-context comments on strings), shared TMs, and glossaries.
- Feedback: Regularly provide feedback among translators, editors, and project managers. Use the CAT tool’s features to track revisions and comments.
- Manage workloads: Use the tool’s project management aspects (if available) to assign tasks, monitor deadlines, and allocate resources.
- Automate repetitive tasks: Identify and automate tasks like pre-translation with TM matches, basic QA checks, file formatting, and even content import/export through integrations.
Conclusion
You have now explored Computer-Assisted Translation in detail: from the primary features that drive efficiency and quality, to the practical steps for the right tool selection and its potential maximization. Knowing the difference between CAT and TMS helps you select the best technology for to your translation/localization needs.
Quality efficient translation management and multilingual content creation don’t just rely on individual skill, but on the tools, systems, and workflows that are being utilized in a project.
If you see that CAT and TMS integrated platform is an interesting solution for your business/project, you should check out the following pages:
- Pricing: view our pricing and find the best plan for you;
- Watch a Demo: see how does Crowdin Software work;
- Book a Demo Call: talk to our specialist and explore how Crowdin can benefit your project.
Yana Feshchuk
Yana Feshchuk is a Partnerships Marketing Manager. Her expertise lies in developing authoritative and well-researched content for the localization field.
